
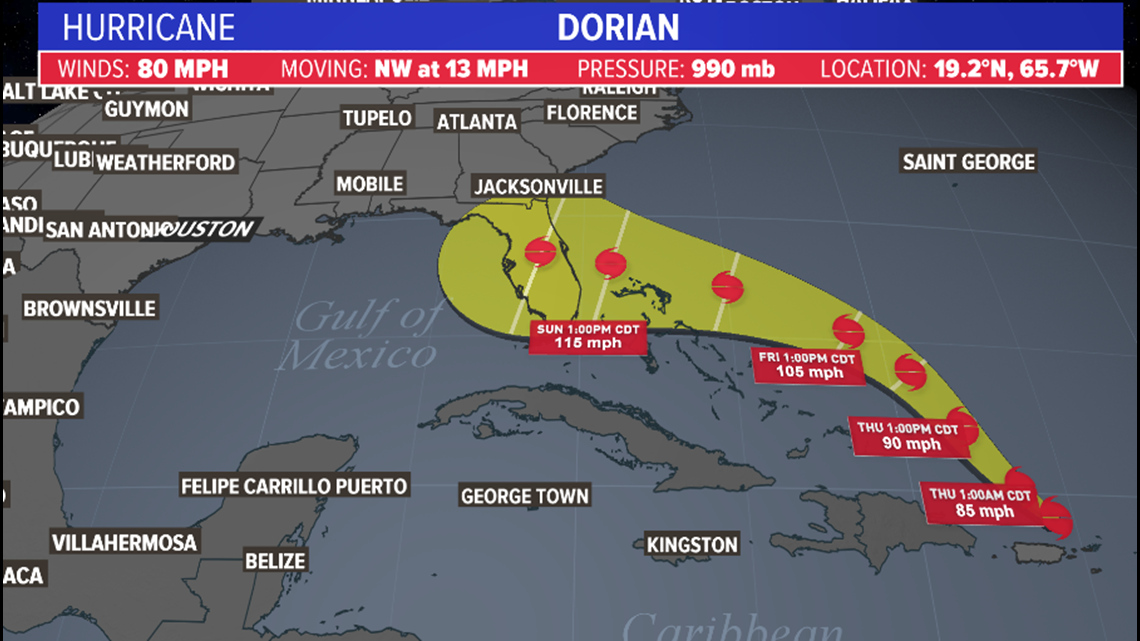
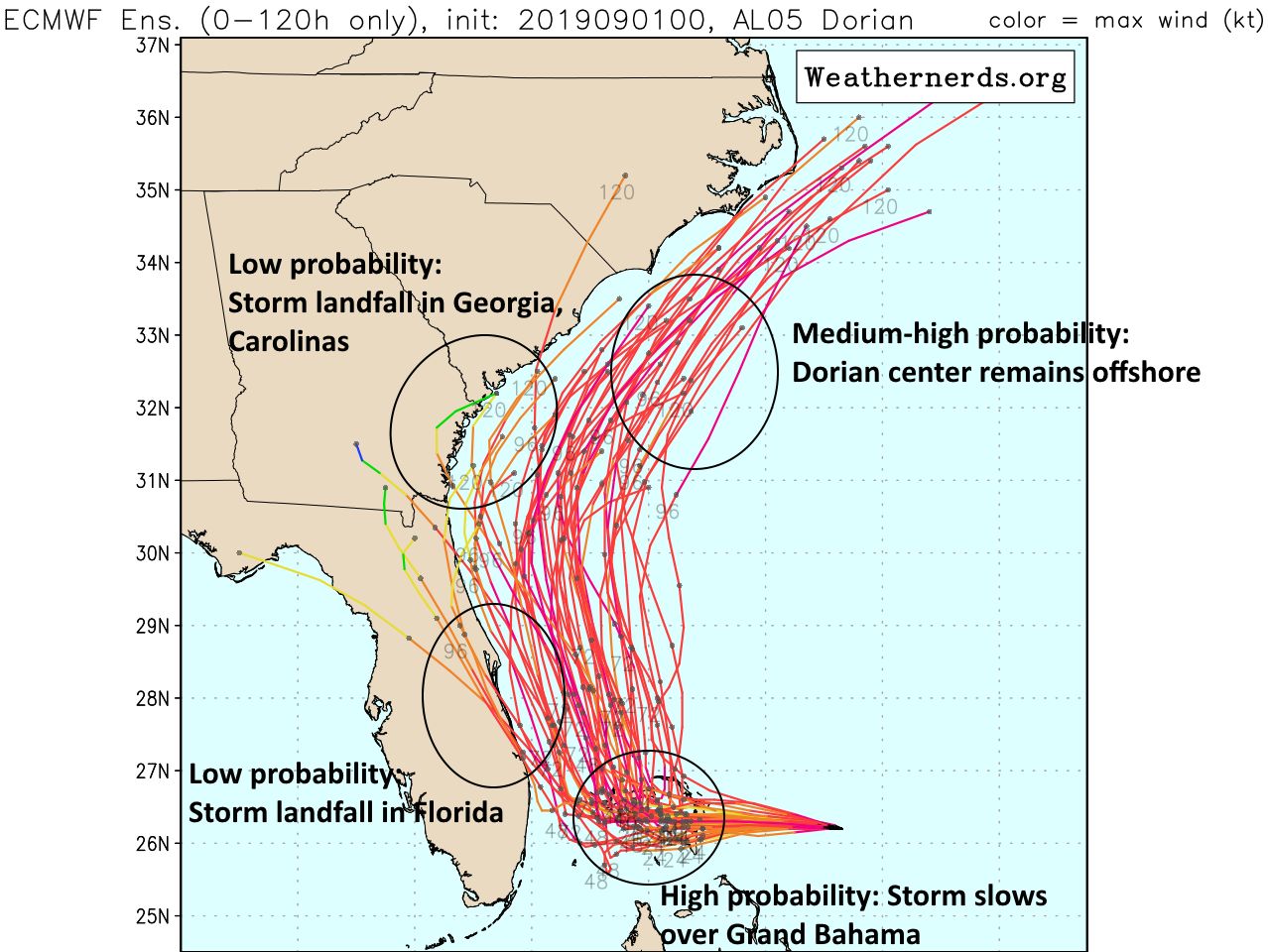
It would have a hard time putting the pieces back together and strengthening before its arrival this weekend in Florida. That would destroy the storm's structure and circulation, crippling the system as it enters the Bahamas. If the core of Dorian moves slightly west of there, over the center of Haiti and the Dominican Republic, it will encounter towering mountainous terrain with elevations over 5,000 feet. Dorian could pass through the Mona Passage, a narrow ocean channel separating Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic. The consensus forecast of both the National Hurricane Center and the various computer models shows a most likely track in between the two islands, right through the 80-mile-wide Mona Passage. The small size of the storm may even allow it to strengthen some, as the official forecast from the National Hurricane Center calls for, through Wednesday. Given the system's tenacity so far, it seems Dorian will survive its track northwestward toward Puerto Rico. Satellite imagery shows Tropical Storm Dorian heading toward Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, at top left. This 80-mile wide ocean corridor, which sits between the islands of Hispañiola and Puerto Rico, will determine if Dorian dissipates or perseveres.ĭorian is now located in the Caribbean, a small storm surrounded by a hostile environment of abundant dry air.Īs seen in the graphic below, it is likely the small size of Dorian has helped to insulate the storm, in a cocoon of sorts, from the outside environment of not only dry air but also strong winds ahead of the system, which would otherwise tear Dorian apart. The future of Dorian largely hinges on one key factor called the Mona Passage.

While this storm is not expected to become a behemoth like Hurricane Maria or Irma, there is a chance this could be a significant system when it reaches Florida this weekend. The forecast track from each model is represented by a line - with all of them checked constantly for changes, trends and consistency.Tropical Storm Dorian poses the first big threat of the hurricane season to the Caribbean and Florida. The models are run and operated by governments and private companies around the world.įor example, the Navy Global Environmental Model is run by the US Navy’s Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center.Īmong the more familiar models are the American (GFS) and European (ECMWF) models, which are run by the US government and a partnership of European countries, respectively. Statistical models are based on historical relationships between a hurricane’s behavior and storm-specific details such as location and date.Įnsemble, or consensus, models are created by combining the forecasts from a variety of other models. There are three kinds of spaghetti models - dynamical, statistical and ensemble.ĭynamical models require hours of numbers-crunching by a supercomputer to solve physical equations of motion. The more the lines are clustered together, the higher the likelihood the storm will hit its expected target. The long-range forecast models are known colloquially as spaghetti plots because of the multiple strings that are generated by some of the fastest computers on Earth, according to CNN. 'Miracle' dog found alive in debris a month after Hurricane Dorian hit BahamasĮxperts are using their noodles to figure out where Hurricane Dorian will make landfall - by studying spaghetti models.

Trump's Hurricane Dorian tweets caused fury among federal employeesĭamaged caused by Hurricane Dorian totals $3.4B in the BahamasĬows swept away during Hurricane Dorian found alive on tiny island


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
